Antifungal drug eliminates sleeping bowel cancer cells in mice
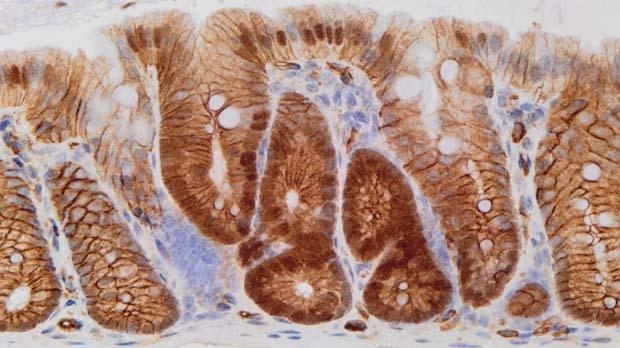
An antifungal medication, commonly prescribed for toenail infections, could help eliminate dormant cells within bowel tumours, according to new research funded by Cancer Research UK and published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine today (Thursday).
Researchers at the Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute have shown in laboratory studies in mice, that itraconazole effectively halts the growth and progression of certain types of bowel cancer. The next step will be to see if this holds true in patients with the disease.
Dr Simon Buczacki, co-lead author and Cancer Research UK clinician scientist, said: “One of the biggest challenges in treating any cancer is the diversity of different cells within the same tumour. We’ve targeted a type of cell that lies asleep within bowel tumours, remaining unresponsive to treatment and putting the patient at risk of their cancer coming back.”
The Cambridge team characterised the molecular nature of dormant bowel cancer cells. These ‘sleeping’ cells are resistant to drugs, including chemotherapy, which work by targeting cells that are actively growing. So even if it looks like a treatment has worked, some of these dormant cells can later awaken after treatment has finished and lead to the tumour re-growing.
The presence of drug-resistant, dormant tumour cells is a problem in many types of cancer. If we find ways to target these cells in bowel cancer, it might provide insights into tackling the problem of dormant tumour cells more broadly.
Prof Greg Hannon, Director of the Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute
The scientists identified two key pathways* involved in cell dormancy and used miniature bowel tumours grown from the cells of mice with cancer, to test different drugs targeting these pathways.
They found, for the first time, that itraconazole blocked signals from a pathway called Wnt, which is implicated in the growth and spread of many different cancers. This led to the tumours collapsing in the mice – dormant cells disappeared and the tumour stopped growing.
“What’s interesting is that this drug seems to kick both dormant and non-dormant cells into action,” added Dr Simon Buczacki. “It forces cells back into a short cycle of growth before slamming on an irreversible ‘stop’ button, entering a permanent standstill that’s known as senescence.”
The next stage will be to test this drug in people. The researchers hope to set up a clinical trial where they can test its effect on patients with hard to treat advanced bowel cancer. They also intend to investigate whether this drug could be more effective in combination with other treatments like chemotherapy.
Professor Greg Hannon, director of the Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, said: “This innovative study has taken a step toward addressing one of the biggest challenges in cancer research. Tumours are made up of many different types of cancer cells, which can evolve separately and respond to treatments differently.
“The presence of drug-resistant, dormant tumour cells is a problem in many types of cancer. If we find ways to target these cells in bowel cancer, it might provide insights into tackling the problem of dormant tumour cells more broadly.”
Related News
See all news-
New immune pathway offers treatment hope for childhood brain tumours
3rd February 2026
A newly discovered immune pathway could lead to gentler treatments for multiple childhood brain cancers, according to new research from our Gilbertson Group published today in Nature Genetics.
Find out more -
Targeting paused cells could improve chemotherapy for lung and ovarian cancers
3rd February 2026
New research published today in Nature Aging by scientists at the University of Cambridge sheds light on why some lung and ovarian cancers stop responding to chemotherapy, and how this resistance might one day be prevented.
Find out more -
Hot flush treatment has anti-breast cancer activity, study finds
5th January 2026
A drug mimicking the hormone progesterone has anti-cancer activity when used together with conventional anti-oestrogen treatment for women with breast cancer, a new Cambridge-led trial has found.
Find out more